Lv. 2 게임 맵 최단거리 - 실패
내풀이 (1) : 정확도 55% : DFS는 최단거리구하기에 적합하지 않다.
BFS로 다시 풀어볼것.
class Solution {
int N = 0;
int M = 0;
int[][] map = {};
boolean[][] visited = {};
int count = 0;
int[][] dir = {{1,0},{0,1},{-1,0},{0,-1}};
boolean isPossible = false;
int shortest = 10000;
public int solution(int[][] maps) {
int answer = 0;
N = maps.length;
M = maps[0].length;
map = maps;
visited = new boolean[N][M];
dfs(0,0);
if(isPossible == false){
answer = -1;
}else{
answer = shortest;
}
return answer;
}
//x행 y열 칸 dfs 경로 탐색
public void dfs(int x, int y){
//이미 방문했으면 종료, 벽(0)이라면 종료
if(visited[x][y] == true || map[x][y] == 0){
return;
}
//도달했다면 끝내기
if(x == N-1 && y == M -1){
isPossible = true;
count++;
shortest = Math.min(shortest, count);
return;
}
//방문 했음을 갱신
visited[x][y] = true;
count++;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
int nextX = x + dir[i][0];
int nextY = y + dir[i][1];
if(nextX >= 0 && nextX < N && nextY >= 0 && nextY< M){
dfs(nextX,nextY);
}else{
continue;
}
}
}
}참고한풀이
public class shortest_gamemap2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] maps = {{1,0,1,1,1},{1,0,1,0,1},{1,0,1,1,1},{1,1,1,0,1},{0,0,0,0,1}};
shortest_gamemap2 s = new shortest_gamemap2();
System.out.println(s.solution(maps));
}
int[] dx = {-1,0,0,1};
int[] dy = {0,1,-1,0};
boolean[][] visit;
int n,m;
public int solution(int[][] maps){
n = maps.length;
m = maps[0].length;
visit = new boolean[n][m];
return bfs(0,0,maps);
}
public int bfs(int x,int y, int[][] maps){
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(new Node(x,y,1));
visit[x][y] = true;
while(!q.isEmpty()){
Node node = q.poll();
if(node.x == n-1 && node.y == m-1) return node.cost;
for(int i = 0; i<4;i++){
int nx = node.x + dx[i];
int ny = node.y + dy[i];
if(nx>=0 && ny>=0 && nx<n && ny<m){
if(maps[nx][ny]==1 &&!visit[nx][ny]){
visit[nx][ny] = true;
q.offer(new Node(nx,ny, node.cost+1));
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
public class Node{
int x;
int y;
int cost;
public Node(int x, int y, int cost){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.cost = cost;
}
}
}
https://geunzrial.tistory.com/115
[프로그래머스 2단계] 게임 맵 최단거리 [java]
문제 https://programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/1844 코딩테스트 연습 - 게임 맵 최단거리 [[1,0,1,1,1],[1,0,1,0,1],[1,0,1,1,1],[1,1,1,0,1],[0,0,0,0,1]] 11 [[1,0,1,1,1],[1,0,1,0,1],[1,0,1,1,1],..
geunzrial.tistory.com
Lv. 2 예상 대진표 - 성공
내풀이(1) : 정확도 88%
단순히 a와 b가 1차이만 나면 만나는 것으로 착각. 반례) 2와 3은 바로 만날 수 없음.
class Solution
{
public int solution(int n, int a, int b)
{
int answer = 0;
if(a - b == 1 || a - b == -1){
answer = 1;
return 1;
}
if(a % 2 == 1) a = a+1;
if(b % 2 == 1) b = b+1;
int round = 1;
while(b - a != 1 && b - a != -1){
a = a/2;
b = b/2;
if(a - b == 1 || a - b == -1){
round++;
answer = round;
break;
}
if(a % 2 == 1) a = a+1;
if(b % 2 == 1) b = b+1;
round++;
}
answer = round;
return answer;
}
}고친 풀이
class Solution
{
public int solution(int n, int a, int b)
{
int answer = 0;
int round = 1;
while(true){
if( a % 2 == 1) a = a+1;
if( b % 2 == 1) b = b+1;
if( a == b) {
answer = round;
return answer ;
}else{
round++;
a = a/2;
b = b/2;
}
}
}
}
복습할 내용: 스위치 구문에서 BREAK 필수
switch(a){
case '[' :{
count[0]++;
break;
}char 클래스 유형 -> Character (대문자 주의...)
stack.poll() (x) -> stack.pop()
내 풀이 (1) : 정확도 85%
}}}인경우도 성공한 것으로 됨. -> 스택을 이용해서 해결
class Solution {
public int solution(String s) {
int answer = -1;
int count = 0;
char[] arr = s.toCharArray();
char[] temp = {};
for(int i = 0 ; i< s.length(); i++){
temp = moveList(arr,i);
if(isPossible(temp)){
count++;
}
}
answer = count;
if(count == 0) answer = 0;
return answer;
}
public char[] moveList(char[] ch, int k){
char[] temp = new char[ch.length];
for(int i = 0 ; i < ch.length; i++){
temp[(i + k)%ch.length] = ch[i];
}
return temp;
}
public boolean isPossible(char[] list){
int[] count = new int[3];
// Stack<char> stack = new Stack<char>();
for(char a : list){
switch(a){
case '[' :{
count[0]++;
break;
}
case '(' :{
count[1]++;
break;
}
case '{' :{
count[2]++;
break;
}
case ']' :{
if(count[0] != 0){
count[0]--;
}
break;
}
case ')' :{
if(count[1] != 0){
count[1]--;
}
break;
}
case '}' :{
if(count[2] != 0){
count[2]--;
}
break;
}
}
}
for(int a : count){
if(a > 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
}맟춘 내 풀이(2)
class Solution {
public int solution(String s) {
int answer = -1;
int count = 0;
char[] arr = s.toCharArray();
char[] temp = {};
for(int i = 0 ; i< s.length(); i++){
temp = moveList(arr,i);
if(isPossible(temp)){
count++;
}
}
answer = count;
if(count == 0) answer = 0;
return answer;
}
public char[] moveList(char[] ch, int k){
char[] temp = new char[ch.length];
for(int i = 0 ; i < ch.length; i++){
temp[(i + k)%ch.length] = ch[i];
}
return temp;
}
public boolean isPossible(char[] list){
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<Character>();
for(char a : list){
if(!stack.isEmpty()&& stack.peek() == '{' ){
if(a == '}'){stack.pop();}
else { stack.push(a);}
}
else if(!stack.isEmpty()&& stack.peek() == '(' ){
if(a == ')'){stack.pop();}
else { stack.push(a);}
}
else if(!stack.isEmpty()&& stack.peek() == '[' ){
if(a == ']'){stack.pop();}
else { stack.push(a);}
}else{
stack.push(a);
}
}
if(!stack.isEmpty()) return false;
return true;
}
}
Lv. 2 배달 - 성공
다른 정점까지의 최단거리를 계산할 때 BFS를 사용 But 가중치가 1일때 사용함.
복습할내용 : (최단경로알고리즘)Dijkstra 다익스트라
Error) 제네릭 배열은 타입 안전성을 보장할 수 없어 직접 생성이 불가능 -> generic array creation 에러
내풀이 (1) 정확도 25% : 방향성이 있는 상태로 다익스트라 알고리즘을 사용하는 실수. -> 방향성을 없애고 해결.
class Solution {
ArrayList<Edge>[] edges;
int N = 0;
int [] dist = {};
public int solution(int N, int[][] road, int K) {
int answer = 0;
this.N = N;
dist = new int[N+1]; //[start에서 1~N까지의 걸리는 거리]
edges = new ArrayList[N+1]; //1~ N까지의 엣지 리스트
for(int i = 1 ; i <= N ; i++){
edges[i] = new ArrayList<Edge>();
}
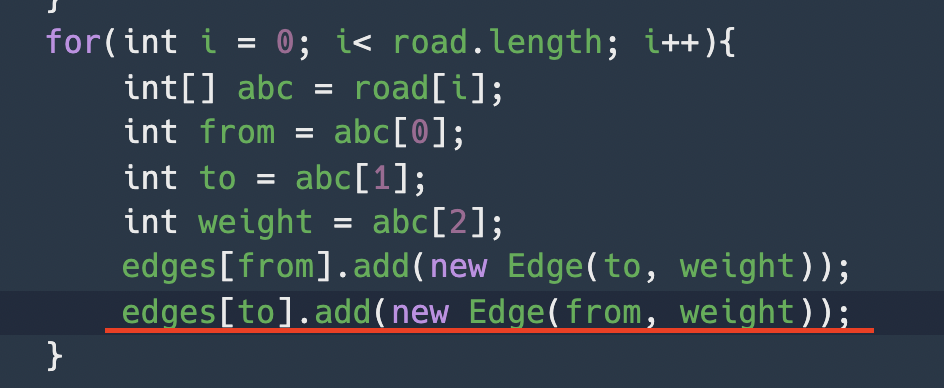
for(int i = 0; i< road.length; i++){
int[] abc = road[i];
int from = abc[0];
int to = abc[1];
int weight = abc[2];
edges[from].add(new Edge(to, weight));
}
dijkstra(1);
for(int time : dist){
if(time <= K){
answer = answer + 1;
System.out.println(time);
}
}
answer = answer -1;
return answer;
}
public void dijkstra(int start){
// 모든 정점까지에 대한 거리를 무한대로 초기화 해주기.
// ※주의사항※
// 문제의 정답으로 가능한 거리의 최댓값보다 큰 값임을 보장해야 한다.
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) dist[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// 최소 힙 생성
PriorityQueue<Info> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(o -> o.dist));
// 다른 방법) PriorityQueue<Info> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o1.dist - o2.dist);
// 시작점에 대한 정보(Information)을 기록에 추가하고, 거리 배열(dist)에 갱신해준다.
pq.add(new Info(start, 0));
dist[start] = 0;
// 거리 정보들이 모두 소진될 때까지 거리 갱신을 반복한다.
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
Info info = pq.poll();
// 꺼낸 정보가 최신 정보랑 다르면, 의미없이 낡은 정보이므로 폐기한다.
if (dist[info.idx] != info.dist) continue;
// 연결된 모든 간선들을 통해서 다른 정점들에 대한 정보를 갱신해준다.
for (Edge e : edges[info.idx]) {
if (dist[info.idx] + e.weight >= dist[e.to]) continue;
// e.to 까지 갈 수 있는 더 짧은 거리를 찾았다면 이에 대한 정보를 갱신하고 PQ에 기록해준다.
dist[e.to] = dist[info.idx] + e.weight;
pq.add(new Info(e.to, dist[e.to]));
}
}
}
}
class Edge{
int to;
int weight;
public Edge(int a, int b){
this.to = a;
this.weight = b;
}
}
class Info{
int idx ; //지점.
int dist;// 거리
public Info(){
}
public Info(int a, int b){
this.idx = a;
this.dist = b;
}
}고친 풀이
class Solution {
ArrayList<Edge>[] edges;
int N = 0;
int [] dist = {};
public int solution(int N, int[][] road, int K) {
int answer = 0;
this.N = N;
dist = new int[N+1]; //[start에서 1~N까지의 걸리는 거리]
edges = new ArrayList[N+1]; //1~ N까지의 엣지 리스트
for(int i = 1 ; i <= N ; i++){
edges[i] = new ArrayList<Edge>();
}
for(int i = 0; i< road.length; i++){
int[] abc = road[i];
int from = abc[0];
int to = abc[1];
int weight = abc[2];
edges[from].add(new Edge(to, weight));
edges[to].add(new Edge(from, weight));
}
dijkstra(1);
for(int time : dist){
if(time <= K){
answer = answer + 1;
System.out.println(time);
}
}
answer = answer -1;
return answer;
}
public void dijkstra(int start){
// 모든 정점까지에 대한 거리를 무한대로 초기화 해주기.
// ※주의사항※
// 문제의 정답으로 가능한 거리의 최댓값보다 큰 값임을 보장해야 한다.
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) dist[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// 최소 힙 생성
PriorityQueue<Info> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(o -> o.dist));
// 다른 방법) PriorityQueue<Info> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o1.dist - o2.dist);
// 시작점에 대한 정보(Information)을 기록에 추가하고, 거리 배열(dist)에 갱신해준다.
pq.add(new Info(start, 0));
dist[start] = 0;
// 거리 정보들이 모두 소진될 때까지 거리 갱신을 반복한다.
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
Info info = pq.poll();
// 꺼낸 정보가 최신 정보랑 다르면, 의미없이 낡은 정보이므로 폐기한다.
if (dist[info.idx] != info.dist) continue;
// 연결된 모든 간선들을 통해서 다른 정점들에 대한 정보를 갱신해준다.
for (Edge e : edges[info.idx]) {
if (dist[info.idx] + e.weight >= dist[e.to]) continue;
// e.to 까지 갈 수 있는 더 짧은 거리를 찾았다면 이에 대한 정보를 갱신하고 PQ에 기록해준다.
dist[e.to] = dist[info.idx] + e.weight;
pq.add(new Info(e.to, dist[e.to]));
}
}
}
}
class Edge{
int to;
int weight;
public Edge(int a, int b){
this.to = a;
this.weight = b;
}
}
class Info{
int idx ; //지점.
int dist;// 거리
public Info(){
}
public Info(int a, int b){
this.idx = a;
this.dist = b;
}
}
참고한 코드 :
GitHub - rhs0266/FastCampus: Fast Campus 강의 관련 자료입니다.
Fast Campus 강의 관련 자료입니다. Contribute to rhs0266/FastCampus development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
Lv. 2 2 x n 타일링 - 성공
복습할 내용 : 동적 프로그래밍
첫번째 풀이(1) : 나머지 처리를 안해서 틀림.
class Solution {
public int solution(int n) {
int answer = 0;
int[] arr = new int[n+1]; //0빼고 1~N까지.
arr[1] = 1;
arr[2] = 2;
for(int i = 3 ; i<= n ; i++){
arr[i] = arr[i-2] + arr[i-1];
}
answer = arr[n];
return answer;
}
}고친풀이(2)
class Solution {
public int solution(int n) {
int answer = 0;
int[] arr = new int[n+1]; //0빼고 1~N까지.
arr[1] = 1;
arr[2] = 2;
for(int i = 3 ; i<= n ; i++){
arr[i] = (arr[i-2] + arr[i-1]) % 1000000007;
}
answer = arr[n];
return answer;
}
}
'알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Algorithm] 6월9일 알고리즘 연습 (프로그래머스 LEVEL2) - 에이젠 (0) | 2022.06.09 |
|---|---|
| [Algorithm] 6월8일 알고리즘 연습 (프로그래머스 level2) - 에이젠 (0) | 2022.06.08 |
| [Algorithm]6월6일 알고리즘 연습 (프로그래머스 level2) - 에이젠 (0) | 2022.06.06 |
| [Algorithm]6월5일 알고리즘 연습(프로그래머스 level2) -에이젠 (0) | 2022.06.05 |
| [Algorithm] 6월2일 알고리즘 연습(프로그래머스 Level2) - 에이젠 (0) | 2022.06.02 |


댓글